Introduction
The plastics pipes industry revolves around specifications and standards for the products and test methods to verify performance. Pipe systems are one of the most critical applications for thermoplastics materials with a design base of 50 years and expected lifetime in excess of 100 years. Products must be fit for purpose and the end user needs confidence in the product in order to specify them. Specifications and dimensions must be universal and methods of test need to be standardised. The industry has put in a great deal of effort over many years to develop reliable methods.
There is an extensive range of ISO (international) and EN (European) Standards covering PE pipes. Technical Committees ISO/TC138 and CEN/TC155 are responsible for ISO and EN Standards respectively for plastics piping systems. All Standards are reviewed every 3 to 5 years and revised and updated if required.
Water & gas pipe renovation or rehabilitation
All rehabilitation works for water mains using polyethylene liner pipes should now be carried out in accordance with the relevant ISO Standards.
There are four general System Standards for renovation using plastics piping systems:
- ISO 11296: Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground non-pressure drainage and sewerage networks.
- ISO 11297: Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground drainage and sewerage networks under pressure.
- ISO 11298: Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground water supply networks.
- ISO 11299: Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground gas supply networks.
These System Standards are distinguished from those for conventionally installed plastics piping systems by the requirement to verify certain characteristics in the as-installed condition, after site processing. This is in addition to specifying requirements for plastics piping systems components as manufactured.
This System Standard comprises a:
- — Part 1: General
and all applicable renovation technique family-related parts from the following:
- — Part 2: Lining with continuous pipes
- — Part 3: Lining with close-fit pipes
- — Part 4: Lining with cured-in-place pipes
- — Part 6: Lining with adhesive-backed hoses
- — Part 7: Lining with spirally-wound pipes
The requirements for any given renovation technique family are given in part 1, applied in conjunction with the relevant other part. For example, ISO 11298-1 and this part of ISO 11298 together specify the requirements relating to lining with close-fit pipes. For complementary information, see ISO 11295. Not all technique families are pertinent to every area of application and this is reflected in the part numbers included in each System Standard.
A consistent structure of clause headings has been adopted for all parts of ISO 11298, in order to facilitate direct comparisons across renovation technique families.
Figure 1 shows the common part and clause structure and the relationship between ISO 11298 and the System Standards for other application areas.
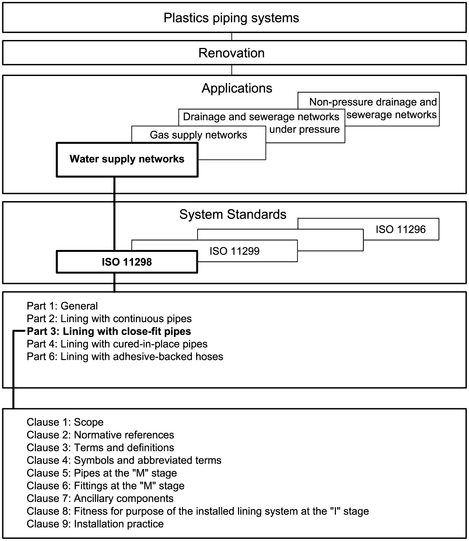
Figure 1 - Format of the renovation System Standards
In addition ISO 11295: Classification and Information on design of plastics piping systems used for renovation applies to all the systems covered by the systems standards: water supply, gas supply, non-pressure drainage and sewerage, and drainage and sewerage under pressure.
A similar suite of Standards is under development for trenchless Replacement, in which the pipe is replaced rather than renovated. This is ISO 21225 and its structure is shown below alongside that for renovation. To date Part 1 has been published (2018).
.png)
National Guidance
Codes of Practice are generally specific to individual countries, industry sectors or utilities. Most asset owners be they national, network or other owners will have their own Codes, Manuals or Guidelines to cover the correct installation practice which must be followed. In addition national Safety and Government legislation exists in most countries and must be followed.
Examples are given below of national guidance that must be followed in the United Kingdom. Similar guidance is applicable in most other countries. Gas works especially are governed by strict safety regulation which applies to all installation and rehabilitation operations. Water works are governed by regulations to protect potable water quality and public health.
Health & Safety Executive
- HSG 47 - Avoiding danger from underground services
- INDG258 - Confined spaces - A brief guide to working safely
- NRSWA - New Roads and Streetworks Act
Institution of Gas Engineers
- IGEM/TD/3 edition 4 – Steel and PE pipelines for Gas distribution
Gas Networks
- T/PR/ML/1 to ML/4 – Work Procedures for pipe system construction
- T/PM/MSL/1 - Management procedure for main laying and service laying
- T/PR/SL/1 - Work procedure for service laying Up to and including 63mm diameter at pressures up to and including 2bar
- GIS/PL2-2: Polyethylene gas pipes & fittings for transport of natural gas and suitable manufactured gas – Part 2: Pipes for use at pressures up to 5.5 bar
- GIS/PL2-4: Polyethylene gas pipes & fittings for transport of natural gas and suitable manufactured gas – Part 4: Fusion fittings with integral heating element(s)
- GIS/PL2-8: Polyethylene gas pipes & fittings for transport of natural gas and suitable manufactured gas – Part 8: Pipes for use at pressures up to 7 bar
Water
- WIS 4-32-08.- Fusion jointing of polyethylene pressure pipeline systems using PE80 and PE100 materials
- The (Water) Regulators Specification & The Water Supply (Water Fittings) Regulations 1999
Related keywords : pe pipe specification, hdpe standards, hdpe pipe fittings standard, poly pipe specs, hdpe water pipe specifications, hdpe pipe and fittings specifications, hdpe pipe specification, hdpe fitting dimensions, iso 472, en pipe standards, hdpe pipeline, hdpe pipe standard, iso 15494, standard pipes, iso pipe standards, polyethylene pipe specifications, hdpe pipe standards, hdpe pipe is code
Product standards for PE pressure piping systems
|
ISO 4427-1 |
Plastics piping systems for water supply, and for drainage and sewerage under pressure – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 1: General |
|
ISO 4427-2 |
Plastics piping systems for water supply, and for drainage and sewerage under pressure – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 2: Pipes |
|
ISO 4427-3 |
Plastics piping systems for water supply, and for drainage and sewerage under pressure – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 3: Fittings |
|
ISO 4427-5 |
Plastics piping systems for water supply, and for drainage and sewerage under pressure – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 5: Fitness for purpose of the system |
|
ISO 4437-1 |
Plastics piping systems for the supply of gaseous fuels – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 1: General |
|
ISO 4437-2 |
Plastics piping systems for the supply of gaseous fuels – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 2: Pipes |
|
ISO 4437-3 |
Plastics piping systems for the supply of gaseous fuels – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 3: Fittings |
|
ISO 4437-4 |
Plastics piping systems for the supply of gaseous fuels – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 4: Valves |
|
ISO 4437-5 |
Plastics piping systems for the supply of gaseous fuels – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 5: Fitness for purpose of the system |
|
EN 1555-1 |
Plastics piping systems for the supply of gaseous fuels –Polyethylene (PE) – Part 1: General |
|
EN 1555-2 |
Plastics piping systems for the supply of gaseous fuels –Polyethylene (PE) – Part 2: Pipes |
|
EN 1555-3 |
Plastics piping systems for the supply of gaseous fuels –Polyethylene (PE) – Part 3: Fittings |
|
EN 1555-4 |
Plastics piping systems for the supply of gaseous fuels –Polyethylene (PE) – Part 4: Valves |
|
EN 1555-5 |
Plastics piping systems for the supply of gaseous fuels –Polyethylene (PE) – Part 5: Fitness for purpose of the system |
|
CEN/TS 1555-7 |
Plastics piping systems for the supply of gaseous fuels –Polyethylene (PE) – Part 7: Guidance for assessment of conformity |
|
EN 12201-1 |
Plastics piping systems for water supply, and for drainage and sewerage under pressure – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 1: General |
|
EN 12201-2 |
Plastics piping systems for water supply, and for drainage and sewerage under pressure – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 2: Pipes |
|
EN 12201-3 |
Plastics piping systems for water supply, and for drainage and sewerage under pressure – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 3: Fittings |
|
EN 12201-4 |
Plastics piping systems for water supply, and for drainage and sewerage under pressure – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 4: Valves |
|
EN 12201-5 |
Plastics piping systems for water supply, and for drainage and sewerage under pressure – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 5: Fitness for purpose of the system |
|
CEN/TS 12201-7 |
Plastics piping systems for water supply, and for drainage and sewerage under pressure – Polyethylene (PE) – Part 7: Guidance for assessment of conformity |
|
ISO 9623 |
PE/metal and PP/metal adapter fittings for pipes for fluids under pressure – Design lengths and size of threads – Metric series |
|
ISO 9624 |
Thermoplastics piping systems for fluids under pressure – Flange adapters and loose backing flanges – Mating dimensions |
|
ISO 15494 |
Plastics piping systems for industrial applications – Polybutene (PB), polyethylene (PE), polyethylene of raised temperature resistance (PE-RT), crosslinked polyethylene (PE-X), polypropylene (PP) – Metric series for specifications for components and the system |
|
ISO 17885 |
Plastics piping systems – Mechanical fittings for pressure piping systems – Specifications |
| ISO 11295 | Plastics piping systems used for renovation of pipelines - Classification & overview of strategic, tactical and operational activities |
| ISO 11296-1 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground non-pressure drainage and sewerage networks. Part 1 General |
| ISO 11296-2 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground non-pressure drainage and sewerage networks. Part 2 Lining with continuous pipes |
| ISO 11296-3 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground non-pressure drainage and sewerage networks. Part 3 Lining with close-fit pipes |
| ISO 11297-1 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground drainage and sewerage networks under pressure. Part 1 General |
| ISO 11297-2 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground drainage and sewerage networks under pressure. Part 2 Lining with continuous pipes |
| ISO 11297-3 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground drainage and sewerage networks under pressure. Part 3 Lining with close-fit pipes |
| ISO 11298-1 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground water supply networks. Part 1 General |
| ISO 11298-2 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground water supply networks. Part 2 Lining with continuous pipes |
| ISO 11298-3 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground water supply networks. Part 3 Lining with close-fit pipes |
| ISO 11299-1 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground gas supply networks. Part 1 General |
| ISO 11299-2 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground gas supply networks. Part 2 Lining with continuous pipes |
| ISO 11299-3 | Plastics piping systems for renovation of underground gas supply networks. Part 3 Lining with close-fit pipes |
Standards for jointing and installation of PE piping systems |
|
|
ISO 12176-1 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Equipment for fusion jointing polyethylene systems – Part 1: Butt fusion |
|
ISO 12176-2 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Equipment for fusion jointing polyethylene systems – Part 2: Electrofusion |
|
ISO 12176-3 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Equipment for fusion jointing polyethylene systems – Part 3: Operator's badge |
|
ISO 12176-4 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Equipment for fusion jointing polyethylene systems – Part 4: Traceability coding |
|
ISO 13761 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Pressure reduction factors for polyethylene pipeline systems for use at temperatures above 20°C |
|
ISO 13950 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Automatic recognition systems for electrofusion joints |
|
ISO 21307 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Butt fusion jointing procedures for polyethylene (PE) piping systems |
|
ISO/TS 10839 |
Polyethylene pipes and fittings for the supply of gaseous fuels – Code of practice for design, handling and installation |
|
EN 12007-2 |
Gas infrastructure - Pipelines for maximum operating pressure up to and including 16 bar – Part 2: Specific functional requirements for polyethylene (MOP up to and including 10 bar) |
| ISO 21225-1 | Plastics piping systems for the trenchless replacement of underground pipeline networks Part 1: Replacement on the line by pipe bursting and pipe extraction |
Test standards for PE piping systems
|
|
|
ISO 1133-1 |
Plastics – Determination of the melt mass-flow rate (MFR) and melt volume-flow rate (MVR) of thermoplastics – Part 1: Standard method |
|
ISO 1167-1 |
Thermoplastics pipes, fittings and assemblies for the conveyance of fluids – Determination of the resistance to internal pressure – Part 1: General method |
|
ISO 1167-2 |
Thermoplastics pipes, fittings and assemblies for the conveyance of fluids – Determination of the resistance to internal pressure – Part 2: Preparation of pipe test pieces |
|
ISO 1167-3 |
Thermoplastics pipes, fittings and assemblies for the conveyance of fluids – Determination of the resistance to internal pressure – Part 3: Preparation of components |
|
ISO 1167-4 |
Thermoplastics pipes, fittings and assemblies for the conveyance of fluids – Determination of the resistance to internal pressure – Part 4: Preparation of assemblies |
|
ISO 1183-1 |
Plastics – Methods for determining the density of non-cellular plastics – Part 1: Immersion method, liquid pyknometer method and titration method |
|
ISO 1183-2 |
Plastics – Methods for determining the density of non-cellular plastics – Part 2: Density gradient column method |
|
ISO 2505 |
Thermoplastics pipes – Longitudinal reversion – Test method and parameters |
|
ISO 3126 |
Plastics piping systems – Plastics components – Determination of dimensions |
|
ISO 4433-1 |
Thermoplastics pipes – Resistance to liquid chemicals – Classification – Part 1: Immersion test method |
|
ISO 4433-2 |
Thermoplastics pipes – Resistance to liquid chemicals – Classification – Part 2: Polyolefin pipes |
|
ISO 6259-1 |
Thermoplastics pipes – Determination of tensile properties – Part 1: General test method |
|
ISO 6259-3 |
Thermoplastics pipes – Determination of tensile properties – Part 3: Polyolefin pipes |
|
ISO 6964 |
Polyolefin pipes and fittings – Determination of carbon black content by calcination and pyrolysis – Test method |
|
ISO 9080 |
Plastics piping and ducting systems – Determination of the long-term hydrostatic strength of thermoplastics materials in pipe form by extrapolation |
|
ISO 9969 |
Thermoplastics pipes – Determination of ring stiffness |
|
ISO 11357-6 |
Plastics – Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) – Part 6: Determination of oxidation induction time (isothermal OIT) and oxidation induction temperature (dynamic OIT) |
|
ISO 11413 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Preparation of test piece assemblies between a polyethylene (PE) pipe and an electrofusion fitting |
|
ISO 11414 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Preparation of polyethylene (PE) pipe/pipe or pipe/fitting test piece assemblies by butt fusion |
|
ISO 12162 |
Thermoplastics materials for pipes and fittings for pressure applications – Classification, designation and design coefficient |
| |
|
|
ISO 13477 |
Thermoplastics pipes for the conveyance of fluids – Determination of resistance to rapid crack propagation (RCP) – Small-scale steady-state test (S4 test) |
|
ISO 13478 |
Thermoplastics pipes for the conveyance of fluids – Determination of resistance to rapid crack propagation (RCP) – Full-scale test (FST) |
|
ISO 13479 |
Polyolefin pipes for the conveyance of fluids – Determination of resistance to crack propagation – Test method for slow crack growth on notched pipes |
|
ISO 13480 |
Polyethylene pipes – Resistance to slow crack growth – Cone test method |
|
ISO 13951 |
Plastics piping systems – Test method for the resistance of plastic pipe/pipe or pipe/fitting assemblies to tensile loading |
|
ISO 13953 |
Polyethylene (PE) pipes and fittings – Determination of the tensile strength and failure mode of test pieces from a butt-fused joint |
|
ISO 13954 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Peel decohesion test for polyethylene (PE) electrofusion assemblies of nominal outside diameter greater than or equal to 90 mm |
|
ISO 13955 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Crushing decohesion test for polyethylene (PE) electrofusion assemblies |
|
ISO 13956 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Decohesion test of polyethylene (PE) saddle fusion joints – Evaluation of ductility of fusion joint interface by tear test |
|
ISO 13957 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Polyethylene (PE) tapping tees – Test method for impact resistance |
|
ISO 13968 |
Plastics piping and ducting systems – Thermoplastics pipes – Determination of ring flexibility |
|
ISO 15512 |
Plastics – Determination of water content |
|
ISO 16871 |
Plastics piping and ducting systems – Plastics pipes and fittings – Method for exposure to direct (natural) weathering |
|
ISO 17778 |
Plastics piping systems – Fittings, valves and ancillaries – Determination of gaseous flow rate/pressure drop relationships |
|
ISO 18553 |
Method for the assessment of the degree of pigment or carbon black dispersion in polyolefin pipes, fittings and compounds |
| |
|
|
ISO 21751 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Decohesion test of electrofusion assemblies – Strip-bend test |
|
EN 12099 |
Plastics piping systems – Polyethylene piping materials and components – Determination of volatile content |
|
EN 12106 |
Plastics piping systems – Polyethylene (PE) pipes – Test method for the resistance to internal pressure after application of squeeze-off |
| ISO 16770 | Accelerated Full Notch Creep test for environmental stress cracking (ESC) |
| ISO 18488 | Strain hardening modulus for slow crack growth (SCG) |
| ISO 18489 | Cracked round bar test for slow crack growth |
Other useful reference standards for PE |
|
|
ISO 3 |
Preferred numbers – Series of preferred numbers |
|
ISO 472 |
Plastics – Vocabulary |
|
ISO 1043-1 |
Plastics – Symbols and abbreviated terms – Part 1: Basic polymers and their special characteristics |
|
ISO 4065 |
Thermoplastics pipes – Universal wall thickness table |
|
ISO 11922-1 |
Thermoplastics pipes for the conveyance of fluids – Dimensions and tolerances – Part 1: Metric series |
|
ISO 14040 |
Environmental management – Life cycle assessment – Principles and framework |
|
ISO/TR 10358 |
Plastics pipes and fittings – Combined chemical resistance classification table |
| BS 9295 | Guide to the structural design of buried pipes |
Standards referred to in the PE Pipe Model
The plastics pipes industry revolves around specifications and standards for the products and test methods to verify performance. Pipe systems are one of the most critical applications for thermoplastics materials with a design lifetime of 50 years and expected lifetime in excess of 100 years. Products must be fit for purpose and the end user needs confidence in the product in order to specify them. Specifications and dimensions must be universal and methods of test need to be...
Top articles
PE100+ position letter on ANPT
(SCG) resistance on pipes for pressure applications since many years. With the introduction of PE 100-RC materials in EN 1555, EN 12201 and ISO...
PE 100-RC+ Quality Materials List
PE 100-RC+ materials have become an essential and well established sub-family of PE 100 compounds. They have a higher stress crack resistance and...
PE 100+ association leads permeation tests for H2 ready certification
A number of gas utilities and grid owners have approached the PE 100+ association regarding the suitability of PE 100 pipe systems for the...
Why choose PE compounds for pressure pipe ?
Simplicity or consistency There are two approaches to PE100 pipe manufacture: Fully compounded. The polymer producer manufactures and supplies to...
PE100+ Quality Materials List
PE100+ Quality Materials List is valid until 31st of March 2026. It is available online and a PDF version can be downloaded at the bottom of this...
Testing methods
Creep rupture strength - Internal pressure test Constant internal pressure at constant temperature The internal pressure test is standardised in ISO...
Pipe Reaming
PIPE REAMING - TECHNIQUE Pipe reaming , also known as pipe eating , is a trenchless pipe replacement technique that removes the host pipe while at...
Pipe Bursting and Splitting
PIPE BURSTING / SPLITTING - TECHNIQUE Pipe bursting and pipe splitting are trenchless methods used to replace existing pipelines with PE100 or...
What range of pipe dimensions is available?
PE100 can be manufactured in a wide range of polyethylene pipe diameters from 16mm to 2000mm. Even larger diameters are possible with the...

